Guide to Open And Close Ports on CentOS 6/7
Looking for commands to Open and Close ports on your Linux Machine? It is very easy and needs no expert knowledge. This small guide will show you how you can open and close ports on CentOS 6/7.

Let’s start how we can open and close ports on your Linux Server with CentOS 6/7.
Requirements
- Root Access for the server
Procedure
Open Port in CentOS 6
- Log in to the root of your server
- Run the following commands to open port 5555
/sbin/iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --destination-port 5555 -j DROP
/sbin/service iptables save
iptables -S
Close Port in CentOS 6
- Log in to the root of your server.
- Run the following commands to close port 5555
/sbin/iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --destination-port 5555 -j DROP
/sbin/service iptables save
iptables -S
Open Port in CentOS 7
- Log in to the root of your server.
- Run the following commands to open 5555
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=5555/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
Close Port in CentOS 7
- Log in to the root of your server.
- Run the following commands to close 5555
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --remove-port=5555/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
With this, we finish the guide for opening and closing ports on the CentOS server.
How to check if a particular port is open?
- In terminal type the following command to check open port. For Example, we tried checking Port 22 on our server.
netstat -lntu | grep 22

If the port is open then this will show the details for the port along with the protocol used.
If you see no output then that means the port is not open or running on your Linux Machine - If you want to check all the open ports then kindly run the following command
netstat -lntu
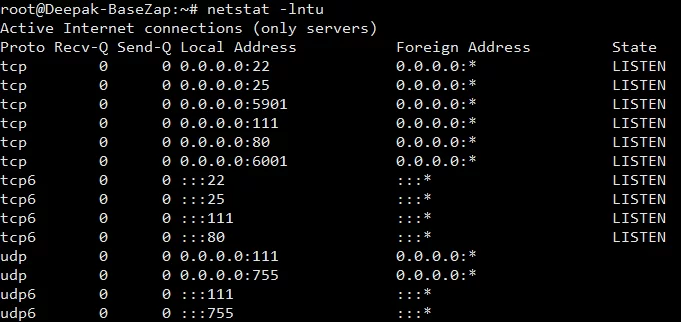
This will list all open ports or currently running ports including TCP and UDP in your Linux Machine.
Check out more guides for Linux/Unix here – https://www.basezap.com/category/linux-unix/





